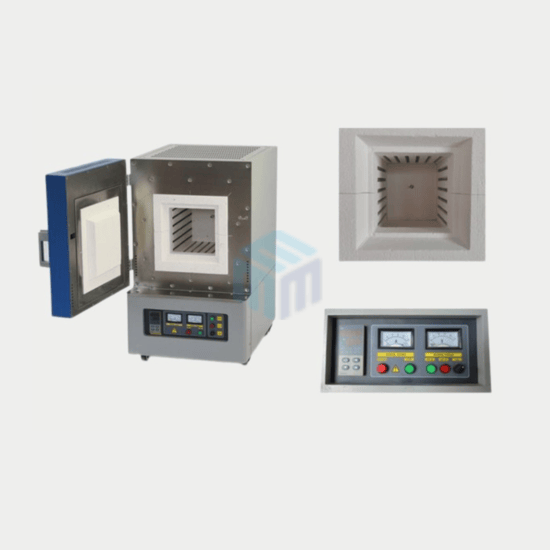
Laboratory furnaces are essential equipment in research, quality control, and industrial applications. Whether you’re working in material science, chemistry, or pharmaceuticals, selecting the right furnace is crucial for achieving precise and reliable results. With various types and specifications available, making an informed decision ensures efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key factors to consider when choosing a laboratory furnace for your research.
1. Understanding Your Laboratory Furnace Application Needs
Different lab furnaces are designed for specific research environments and material processing requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
-
Muffle Furnaces
Ideal for ashing, heat treatment, and material testing in ambient air conditions. A high temperature muffle furnace provides uniform heat distribution, making it suitable for consistent and repeatable results in laboratories working with ceramics, glass, and metals.
-
Tube Furnaces
Best for heating samples under controlled atmospheres or vacuum conditions. These furnaces are often used in chemical synthesis, thermal decomposition, and advanced material research where precision and gas flow control are critical.
-
Vacuum Furnaces
Suitable for sensitive materials or applications requiring high purity and minimal contamination. They are commonly used in metallurgy, aerospace, and semiconductor industries to process materials in a completely oxygen-free environment.
-
Chamber Furnaces
Used for large sample heating and high-temperature applications in metallurgy, ceramics, and material science. They offer excellent temperature uniformity and are built to handle heavy-duty workloads.
-
Elevating/Lifting Furnace
Designed for applications requiring precise loading and unloading of samples at elevated temperatures. The lift mechanism ensures safety and ease when handling delicate or bulky materials.
-
CVD Furnace
Ideal for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes used in semiconductor and advanced material research. These furnaces allow thin-film coating and surface modification under controlled atmospheres.
-
Microwave Furnace
Utilize microwave energy for rapid and uniform heating, significantly reducing processing time. Commonly used in ceramics, sintering, and specialized lab applications requiring energy-efficient heating.
Understanding the nature of your samples, temperature requirements, and atmosphere conditions will help you narrow down your choices.
2. Temperature Range & Uniformity
Temperature capabilities vary significantly across furnace models. Ensure that the furnace you choose can reach the necessary temperatures for your experiments. Common temperature ranges include:
-
Up to 1100°C
– Suitable for basic applications like drying and low-temperature heat treatment.
-
1100°C – 1700°C
– Ideal for ceramic processing, material testing, and high-temperature reactions.
-
Above 1700°C
– Used in advanced material research and metallurgy.
Uniform temperature distribution is another critical factor, as it ensures consistent heating and reliable results.
3. Furnace Capacity & Size
The furnace size depends on the volume of materials you need to process. Consider:
-
Internal Chamber Dimensions
– Ensure your samples fit comfortably inside.
-
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
– If you need high-throughput experiments, consider a larger or continuous-operation furnace.
-
Space Constraints
– Assess the available laboratory space for proper installation and ventilation.
-
Tilting Furnaces
– Useful for melting and pouring applications, providing ease of material handling and enhanced efficiency.
-
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) Furnaces
– Ideal for advanced material processing, enabling thin-film coating and controlled deposition for research and industrial applications.
4. Heating Elements & Insulation
Different heating elements affect performance and durability. Common types include:
-
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
– Fast heating and long lifespan, suitable for high temperatures.
-
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
– Used in ultra-high-temperature furnaces above 1600°C.
-
Nickel-Chrome (NiCr) Alloys
– Suitable for lower temperatures and cost-effective applications.
Insulation materials, such as ceramic fiber or refractory brick, play a role in heat retention and energy efficiency.
5. Atmosphere Control & Safety Features
Some applications require specific gas atmospheres, such as nitrogen, argon, or vacuum conditions. Features to look for include:
-
Gas Flow Control & Sealing
– Prevents contamination and ensures a stable environment.
-
Overheat Protection & Alarms
– Enhances safety and prevents damage.
-
User-Friendly Controls
– Digital interfaces with programmable settings allow precise temperature control.
6. Compliance with Global Standards (India,Australian, US, etc.)
Laboratory furnaces must comply with relevant safety and performance standards. Ensure your equipment meets:
-
AS/NZS 3820
– Electrical safety requirements for laboratory equipment.
-
ISO 9001 Certified Manufacturers
– Ensures quality and reliability.
-
Workplace Safety Regulations
– Verify compatibility with laboratory ventilation and fire safety standards.
7. Energy Efficiency & Cost Considerations
Energy consumption impacts operating costs. Look for energy-efficient models with features like:
-
Low Heat Loss Designs
– Minimizes energy waste.
-
Programmable Schedules
– Reduces unnecessary operation time.
-
Long-Lasting Components – Ensures durability and lowers maintenance costs.
Balancing upfront investment with long-term operational efficiency will help you choose a cost-effective furnace.
Also Read: Maximizing Efficiency with Modern Laboratory Furnaces
Summary
Choosing the right laboratory furnace is vital for accurate and consistent research results. Whether it’s a tube furnace, box furnace, or vacuum furnace, match your selection to your application needs like atmosphere, temperature, and sample size.
If considering a muffle furnace, ensure the muffle furnace temperature suits your process, and compare models by muffle furnace price for the best value. Also explore chamber, CVD, microwave, and elevating furnaces based on your specific requirements.
At M-Kube, we offer a range of laboratory furnaces that meet Global standards and deliver top-tier performance. Contact us today to explore our selection and find the perfect furnace for your research needs. M-Kube experts have more than 15 years of experience in all these furnaces and can provide you the right guidance in your selection.